Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) are key components in electronic circuits for surge protection. With the ongoing trend of miniaturization and higher integration in electronics, the packaging types and performance requirements for MOVs have become increasingly diverse. From traditional radial leaded types to surface-mounted devices (SMDs), the packaging form directly impacts assembly methods, surge handling capability, physical size, and application scenarios.
This article provides a detailed overview of common MOV packaging types, part numbering conventions, performance comparisons, and selection suggestions, with reference to Boarden’s MOV product portfolio.
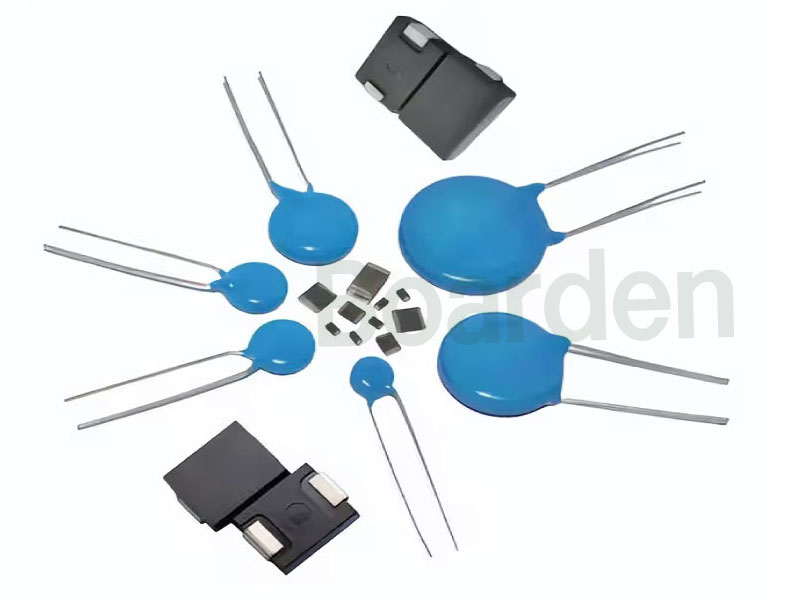
1. Main Packaging Types of MOVs
Radial Leaded MOV
- Structure: Disk-shaped ceramic varistor body with two radial lead wires extending from the bottom.
- Mounting: DIP (through-hole soldering)
- Typical Series: 5D, 7D, 10D, 14D, 20D
- Advantages: High surge current capability, cost-effective, suitable for designs with fewer space constraints.
- Applications: LED lighting, power adapters, energy meters, motor drivers.
Surface-Mount MOVs (SMD MOV / MLV)
SMD MOVs are mainly available in two structural types: epoxy-coated and multilayer ceramic (MLV).
Epoxy-coated SMD MOVs
- Structure: A downsized ceramic MOV disk encapsulated in epoxy, shaped into a rectangular SMD package.
- Features: Combines the robust surge handling of traditional MOVs with SMT compatibility.
- Advantages: Offers higher surge current capacity than MLV; ideal for AC input protection and LED drivers.
- Example Products: Boarden CMS3025 and CMS4032 series, widely used in lighting power supplies and industrial circuits.
Multilayer Ceramic Varistors (MLV)
- Structure: Multiple ceramic layers with alternating internal electrodes, terminated with end caps.
- Features: Compact size, fast response, low clamping voltage; well-suited for high-density circuit boards.
- Advantages: Fully compatible with automated SMT production; ideal for USB ports, signal line protection, and wearable electronics.
- Boarden Products: CMS1206V511-G3, CMS0805V561P300 — known for excellent stability and low leakage.
Special Packages (High Surge / Hybrid Structures)
- Large SMD MOVs: e.g., CMS3025, CMS4032 — high surge capability in compact form for LED drivers and industrial power circuits.
- Square Radial MOVs: Designed for rectifier bridge input protection, such as MOV-S14 and MOV-S20.
2. Packaging Comparison & Selection Guide
| Packaging Type | Mounting | Surge Current | Board Space | SMT Automation | Cost | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radial (Through-hole) | DIP | High | Large | Poor | Low | Power supplies, lighting |
| SMD (MLV structure) | SMT | Medium | Small | Excellent | Medium | LED drivers, compact electronics |
| SMD (Epoxy-coated) | SMT | Medium-High | Medium | Excellent | Medium | Industrial lighting, AC input |
| High-surge SMD | SMT | High | Medium | Excellent | High | LED drivers, industrial power |
Recommendations:
- For cost-sensitive projects: radial type (e.g., 7D561)
- For compact size and automation: MLV type (e.g., CMS1206V511-G3, CMS0805V561, CMS1206V561)
- For high surge + compact form: Boarden’s high-current CMS series
3. Part Numbering Explanation
Radial MOV Naming (Boarden example)
Example: MOV-7D561K
- 7D: Approx. 7mm disk diameter
- 561: Varistor voltage code (561 = 56 × 10 = 560V)
- K: Voltage tolerance ±10%
SMD MLV Naming (Boarden CMS series)
Example: CMS1206V561P500
- CMS: Ceramic Micro-Surge series (SMD MOV)
- 1206: Package size in inch units (3.2mm × 1.6mm)
- V561: Varistor voltage 560V (561 = 56 × 10)
- P500: Surge current capacity, such as 50A @ 8/20μs
4. Product Comparison Table (Boarden)
| Model | Type | Size (mm) | Varistor Voltage | Surge Current (8/20μs) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOV-7D561K | Radial | Ø7 | 560V | ~A (typ.) | Classic solution for lighting, cost-effective |
| CMS0805V561P300 | SMD | 2.0 × 1.25 | 560V | 30A | Ideal for low-power LED/USB circuits |
| CMS1206V511-G3P500 | SMD | 3.2 × 1.6 | 510V | 50A | G3 upgraded chip, low clamping, stable |
| CMS3025V431P501-B | High-surge SMD | 7.6 × 6.4 | 430V | 500A | Ideal for LED drivers, AC bridge input |
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Which type has higher surge capability — radial or SMD?
A: In general, radial MOVs have higher energy absorption due to larger volume. However, Boarden’s CMS series SMD MOVs support surge currents up to 500A, making them suitable replacements in many applications.
Q2: What does “561” mean in the part number?
A: It’s a voltage code — 561 = 56 × 10 = 560V. Typically used with a “K” suffix to indicate ±10% tolerance.
Q3: Can MOVs be used for continuous operation?
A: No. MOVs are designed for transient suppression. Continuous exposure may lead to thermal runaway or failure. Always pair them with a fuse or fusible resistor.
The packaging type and part numbering scheme of MOVs directly affect product selection and circuit reliability. While traditional radial types remain widely used in lighting and adapters, SMD MOVs — especially MLVs — are increasingly favored in compact, high-density designs.
Boarden offers a full range of MOVs, from classic radial types like 7D and 10D, to advanced CMS ceramic micro-surge series, covering needs from cost-effective to high-reliability designs. For samples or technical support, feel free to contact us via WeChat (4027704).





